UN/CEFACT Verifiable Trade Documents
Introduction
UN/CEFACT is in a unique position to lead as the world transitions to the next generation of scalable, secure, digital infrastructure, as emergent verifiable credentials and surrounding technologies are adopted by global trade and logistics actors. In embracing this opportunity, this project aims to design and promote a suite of lightweight global trade documents specifically targeted at modern, digitally verifiable web usage.
The project will prioritize simplicity and recognizability in order to maximize business usage uptake and implementation efficiency. The targeted list of trade documents will be designed for an opinionated modern technology stack, in alignment with the UN/CEFACT technology architecture strategy, prioritizing unambiguity, coherency and interoperability for implementers.
UN/CEFACT Project Proposal
https://uncefact.unece.org/display/uncefactpublic/Verifiable+Credentials+for+Trade
What is a Trade Document?
In traditional international trade, documents like commercial invoices or bills of lading exist as PDFs or paper forms. This specification takes a different approach: the document is the data itself.
A commercial invoice in this specification is structured JSON data containing buyer, seller, line items, and payment terms. This same data can be:
- Displayed as a human-readable web page
- Rendered as a PDF when needed
- Processed directly by software systems
- Cryptographically signed to prove authenticity
The data and the document are one and the same—just expressed using modern web technologies instead of paper or PDF. When we refer to “verifiable trade documents,” we mean structured, machine-readable data sets that carry the same legal and business meaning as their traditional paper counterparts, but designed for digital-native systems.
Verifiability means the data itself contains cryptographic proof of who issued it and that it hasn’t been tampered with, enabling trust without intermediaries.
Requirements
The project will primarily aim to implement the documents which were targeted by the ICC-DSI KTDDE , and roughly targeted in the same batched order; complete coverage of the full set of the 36 KTDDE documents is considered a success criteria.
The KTDDE specification is considered to be a starting point, but the project does not promise to follow the specification strictly. In particular this is because details are often uncovered during implementation which can be difficult to catch in the logical phase.
Similarly, other document types may be included on the premise that they are a generally applicable document commonly exchanged in international trade and transport use cases.
Technical Architecture
Decentralized, Vendor-Neutral Foundation
In an era of increasing digital transformation and cyber threats, global supply chains require a foundation built on trust and transparency. As recognized by governments worldwide, the trust we place in digital infrastructure must be proportional to its trustworthiness and the consequences of misplaced trust.
This project embraces a decentralized, vendor-neutral approach that enables secure trade digitization without lock-in to proprietary platforms or centralized infrastructure. By adopting open standards, any party can independently implement, verify, and exchange trade documents while maintaining full control over their data and processes.
Opinionated Technology Choices
While the digital transformation of supply chains has been slow and fragmented this specification provides a clear path forward through deliberate, opinionated technology choices that maximize interoperability while minimizing implementation complexity.
Vendor-Neutral Trade Data Verifiability
All trade documents follow the W3C Verifiable Credentials data model , establishing cryptographic trust without centralized authorities. This standard makes digital contractual trust accessible and affordable for anyone on the planet.
Key benefits:
- Independent Verification: Any verifier can validate document authenticity and integrity without contacting the issuer
- Cryptographic Assurance: Modern curve-based digital signatures ensure data hasn’t been tampered with
- Flexible Implementation: Documents can be used as standard JSON when verifiability isn’t required, or as fully verifiable credentials when trust is paramount
- Chain of Trust: Links can be established through relevant claims back to known trust anchors
The project provides specific recommendations on cryptographic suites, signing methods, versioning, and revocation to reduce ambiguity and promote seamless adoption.
Strong Semantics for International Trade
Supply chain organizations often use different words to describe the same concepts—“Shipper” and “Consignor” are used interchangeably, creating ambiguity in international contexts. Traditional approaches require manual interpretation and expensive IT integration efforts.
The UN/CEFACT Verifiable Trade Data approach leverages JSON-LD to provide unambiguous semantic meaning:
- Precise Communication: Terms are explicitly tied to URIs, eliminating interpretation errors
- Automated Understanding: Computers can establish semantic meaning without human intervention
- Cost-Effective Integration: Simpler than traditional data mapping and interpretation
- Global Interoperability: Maps to the UN/CEFACT Web Vocabulary for standardized trade terminology
This semantic layer is especially critical in international trade environments where the same term may have different interpretations across jurisdictions and languages. Implementers may choose to leverage or ignore this layer—it enhances interoperability without imposing additional requirements.
Well-Structured, API-Ready Validation
The project defines core data structures using JSON Schema , providing a robust foundation for both traditional API usage and verifiable credentials:
- Machine-Readable Validation: Ensures data quality at exchange time through automated validation rules
- Included in Verifiability: The schema itself is signed as part of the Verifiable Credential, guaranteeing structural integrity
- Developer-Friendly: Broad ecosystem of tooling for generating documentation, validation code, and interactive forms
- Dual-Purpose Design: Works seamlessly for both “raw JSON” API usage and full verifiable credential implementations
By consuming our own JSON Schema output in the documentation, we demonstrate feasibility and provide a clear adoption path for implementers.
Implementation Flexibility
This specification is designed with a fundamental principle of implementation flexibility. Each technical component provides distinct capabilities but remains optional for basic document exchange.
Technical Components and Their Independence:
-
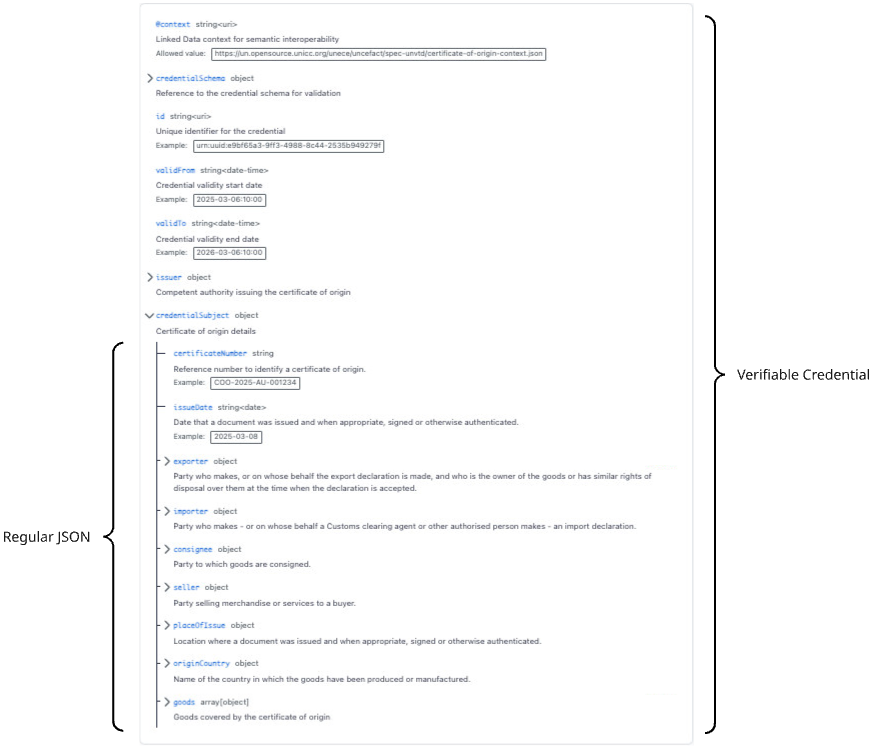
Core Data Model: Each trade document is defined as a structured JSON object conforming to the published JSON Schema. The data model within the
credentialSubjectproperty can be utilized independently in any system or API without requiring additional technical components. -
Semantic Layer: The JSON-LD
@contextprovides machine-readable semantic definitions mapping to the UN/CEFACT vocabulary. Systems not requiring semantic processing may treat the document as standard JSON, with the@contextproperty being safely ignored without affecting data validity. -
Cryptographic Envelope: The W3C Verifiable Credential structure provides cryptographic proof of origin and integrity. This component is entirely optional for implementations that employ alternative trust mechanisms or operate within controlled environments.
Architectural Implications:
- Selective Implementation: Implementers may adopt any combination of components based on their technical requirements and business constraints
- Backward Compatibility: Documents utilizing all components remain processable by systems implementing only the core data model
- Forward Compatibility: Systems initially implementing only core components can incorporate additional capabilities without modifying existing data structures
- Interoperability Preservation: The separation of concerns ensures that systems with different implementation profiles can exchange the fundamental business data
This architectural approach ensures that the specification can accommodate the diverse technical maturity levels and requirements present in global trade ecosystems, from basic data exchange to fully verified, semantically-rich document processing.
Trust Registries
Verifiable credentials provide cryptographic proof of authenticity, but verifiers still need to determine if an issuer is authorized. Trust registries serve as authoritative directories answering: “Is this entity authorized to issue this type of document?”
The UN/CEFACT Global Trust Registry (GTR) develops standards for a global registrar information directory, providing verifiable identifiers for authorized issuers and enabling interoperability between national and sectoral trust frameworks.
Trust registries remain architecturally independent from UNVTD. Organizations may integrate with GTR, use existing trust frameworks, or operate within closed networks based on their requirements.
Normative Design Rules
Issuer Identification
- The
issuerfield must be a simple string ID using the DID URI scheme, not a complex object. The issuing party’s details are represented in the document itself; additional issuer attributes would duplicate information. - All URIs in examples must use the “example” domain (e.g.,
did:web:example.com) to avoid accidentally referencing real companies or authorities. - The issuer DID must match the DID of the appropriate party within the document (e.g., commercial invoice issuer matches seller, bill of lading issuer matches carrier).